Wide receivers (WRs) play a crucial role in football, responsible for catching passes from the quarterback, gaining yardage, and scoring touchdowns. Due to the nature of their position, which involves high-speed sprints, abrupt changes in direction, and physical collisions, wide receivers are particularly prone to certain types of injuries. In this blog, we will explore the most common injuries faced by wide receivers, their causes, and preventive measures.
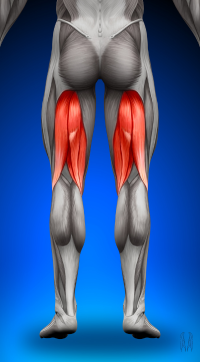
1. Hamstring Strains
Hamstring strains are among the most frequent injuries sustained by wide receivers. These injuries occur when the muscles at the back of the thigh are overstretched or torn, often due to rapid acceleration or deceleration. The explosive sprints and sudden stops that WRs perform make them particularly susceptible to this injury.
Symptoms and Treatment:
Symptoms of a hamstring strain include sharp pain in the back of the thigh, swelling, and difficulty walking or running. Treatment typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Physical therapy may be necessary to strengthen the muscles and prevent future strains.
Prevention:
To prevent hamstring strains, WRs should incorporate regular stretching and strengthening exercises for their hamstrings and surrounding muscles. Warm-ups and cool-downs before and after practice sessions are also crucial.
2. Ankle Sprains
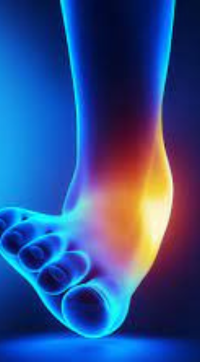
Ankle sprains are another common injury for wide receivers. These occur when the ligaments in the ankle are stretched or torn, often due to sudden changes in direction, jumping, or landing awkwardly. Ankle sprains can vary in severity from mild to severe, affecting a player’s mobility and performance.
Symptoms and Treatment:
Symptoms include pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected ankle. Treatment involves the RICE protocol, and severe cases may require a brace or even surgery. Rehabilitation exercises are essential to restore strength and flexibility.
Prevention:
To prevent ankle sprains, WRs should wear supportive footwear and consider using ankle braces during games and practice. Balance and proprioception exercises can also help strengthen the ankle and improve stability.
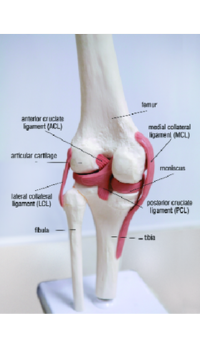
3. ACL Tears
Tears of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) are severe injuries that can sideline a wide receiver for an extended period. The ACL is a cruciate ligament in the knee that stabilizes the joint. ACL tears often occur during sudden changes in direction, pivoting, or awkward landings.
Symptoms and Treatment:
Symptoms include a loud popping sound at the time of injury, severe pain, swelling, and instability in the knee. Treatment usually involves surgical reconstruction of the ACL followed by an extensive rehabilitation program.
Prevention:
Preventing ACL tears involves strengthening the muscles around the knee, particularly the quadriceps and hamstrings. Plyometric exercises and agility drills can also help improve coordination and reduce the risk of injury.
4. Shoulder Dislocations
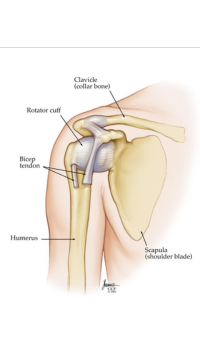
Shoulder dislocations occur when the upper arm bone is forced out of the shoulder socket. This injury is common among wide receivers due to the physical nature of the sport, especially when reaching for a pass or absorbing a tackle.
Symptoms and Treatment:
Symptoms include intense pain, visible deformity, and inability to move the shoulder. Treatment often involves reducing the dislocation (putting the bone back in place) followed by immobilization in a sling. Physical therapy is necessary to restore full function.
Prevention:
Strengthening the shoulder muscles and maintaining good flexibility can help prevent dislocations. WRs should also use proper techniques when catching passes and absorbing tackles to minimize the risk of this injury.
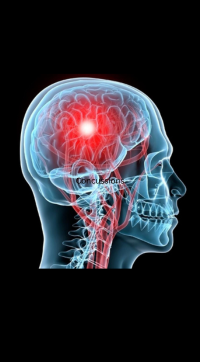
5. Concussions
Concussions are a serious concern in football, including for wide receivers. A concussion is a traumatic brain injury caused by a blow to the head or body, leading to a range of symptoms that can affect cognitive function and physical health.
Symptoms and Treatment:
Symptoms include headache, dizziness, confusion, nausea, and sensitivity to light or noise. Treatment involves rest and gradual return to activity under medical supervision. Severe cases may require extended recovery periods.
Prevention:
To prevent concussions, WRs should always wear properly fitted helmets and follow safe tackling and blocking techniques. Awareness and education about the signs and symptoms of concussions are also crucial for early detection and management.
6. Turf Toe
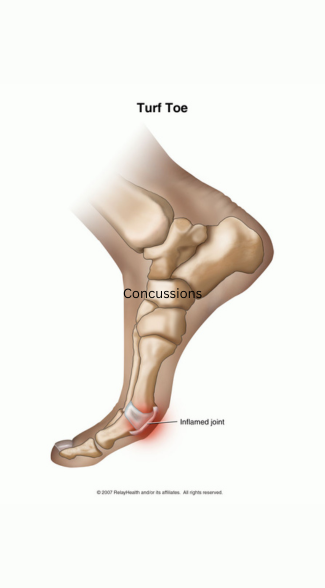
Turf toe is a sprain of the ligaments around the big toe joint, often caused by repetitive hyperextension of the toe during push-offs or sudden stops. This injury is common among wide receivers due to the demands of sprinting and cutting on artificial turf surfaces.
Symptoms and Treatment:
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and limited movement in the big toe. Treatment involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation, along with the use of stiff-soled shoes or orthotics to limit toe movement. Severe cases may require immobilization or surgery.
Prevention:
To prevent turf toe, WRs should wear appropriate footwear that provides adequate support and cushioning. Strengthening exercises for the foot and toe muscles can also help reduce the risk of injury.
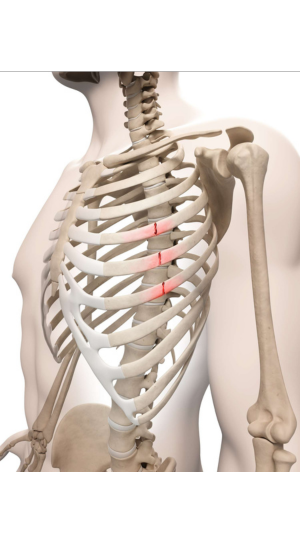
7. Rib Fractures
Rib fractures occur when one or more ribs are cracked or broken, often due to direct impact or collision during a game. Wide receivers are at risk for this injury due to tackles and hits from defenders.
Symptoms and Treatment:
Symptoms include sharp pain in the chest, especially with deep breaths, coughing, or movement. Treatment typically involves rest and pain management, as ribs generally heal on their own over time. Severe cases may require medical intervention.
Prevention:
Wearing rib protectors and padding during games can help reduce the risk of rib fractures. WRs should also work on strengthening their core muscles to provide better support and protection for the ribs.
Wide receivers face a variety of common injuries due to the physical and dynamic nature of their position. Understanding these injuries, their symptoms, and preventive measures is crucial for maintaining the health and performance of wide receivers. Proper training, conditioning, and safety practices can significantly reduce the risk of these injuries, allowing WRs to stay on the field and excel in their roles. By prioritizing injury prevention and effective treatment, wide receivers can ensure a long and successful career in football.







